Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical carbon molecules with an exceptional length-to-diameter ratio. They have novel properties that make them potentially useful in many applications. including extraordinary strength, unique electrical properties and efficient heat conduction.
Carbon nanotubes are molecular-scale tubes of graphitic carbon with outstanding properties. They are among the stiffest and strongest fibres known, and have remarkable electronic properties and many other unique characteristics. For these reasons they have attracted huge academic and industrial interest, with thousands of papers on nanotubes being published every year. Commercial applications have been rather slow to develop, however, primarily because of the high production costs of the best quality nanotubes.
Structure
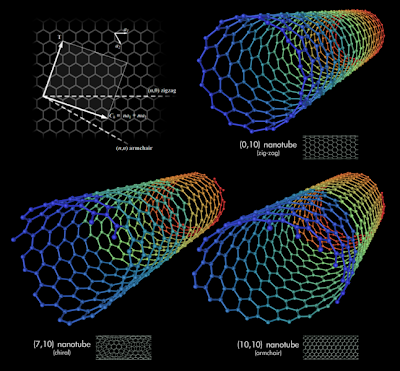
The bonding in carbon nanotubes is sp² , with each atom joined to three neighbours, as in graphite. The tubes can therefore be considered as rolled-up graphene sheets (graphene is an individual graphite layer). There are three distinct ways in which a graphene sheet can be rolled into a tube.
Nanotube science
Nanotube links
Books and Reviews
News
Commercial suppliers
Related:
Carbon Nanotubes
Carbon nanotube - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Nanotube Site
Carbon nanotube radio hints at future wireless - ZDNet UK
New Nanotube Findings Give Boost To Potential Biomedical Applications
Could A Nanotube-based Drug Prevent Radiation Injury?
Physical Properties of Carbon Nanotubes

